WATCH ANATOMY
Welcome to the first part of your watch-buying journey! We believe the more you know, the more confident you’ll be with your purchase. So, got a little time? Check out our quick-and-easy explanation of watch parts, plus common watch terms you may hear when shopping for your next timepiece.

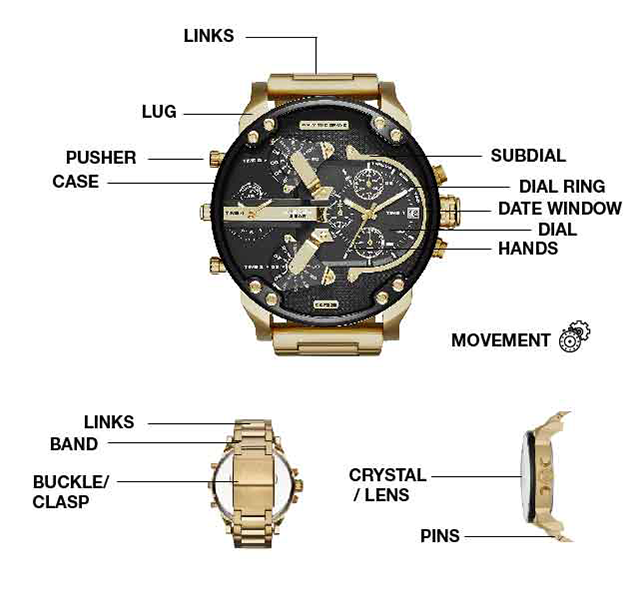
band.
band.
watch function.
protects them, too.
the time or date, and to
wind or stop the
watch.
shows the date.
the band to the lugs, the
links within the band
and the buckle to the band.
two ends of a watch.
There are many different
types of closures.
the dial.
the lens.
the dial.
movement. It displays
the time using numbers,
indices or hands.
of the watch such as
dates, stopwatch
readings and more.
functions of the watch.
Typically, there’s an
hour, minute and second hand.
keeps the time.
WATCH DIALS

The watch face houses the dial, and there are
many different ways it can be marked to show
the passage of time. Here are a few of the most
popular types:

- Stick Indices: No numeral indicator makers
- Arabic: Numeral indicator markers
- Arabic & Stick: Both numerals and stick indices
- Roman: Roman numeral indicators
- Roman & Stick: Both Roman numerals and stick indices
WATCH CASES
Think of the watch case as the bodyguard
for the internal parts of a timepiece. It comes in a
variety of shapes, but the most common are
round,
rectangle, square and oval.


WATCH CRYSTALS

The transparent “glass” that covers the watch face. It helps protect the
internal components from dirt and water. Read on to discover three
major crystal types used when constructing watches.
- Synthetic Sapphire: Developed in the lab, this see-through element
has very similar makeup as sapphire without the high price tag. In other
words? It’s hard as a rock. - Mineral: It’s simple, mineral crystals are made of glass. This type of
watch crystal is relatively inexpensive. - Acrylic: Very similar to plastic, this is the most affordable watch
crystal. This malleable type can be molded into a variety of shapes.

The transparent “glass” that covers the watch
face. It helps protect the internal components
from dirt and water. Read on to discover three
major crystal types used when constructing
watches.
- Synthetic Sapphire: Developed in the lab,
this see-through element has very similar
makeup as sapphire without the high price tag. In other words? It’s hard as a rock. - Mineral: It’s simple, mineral crystals are
made of glass. This type of watch crystal is relatively inexpensive. - Acrylic: Very similar to plastic, this is the most affordable watch crystal. This malleable type can be molded into a variety of shapes.
WATCH BUCKLES & CLASPS

Watch clasps keep your watch securely fastened to your wrist. Here, we’ve rounded up different types you may encounter while watch shopping.
- Butterfly: Similar to a butterfly spreading its wings, the butterfly clasp opens to both the right and left. Found on most bracelet watches.
- Flip: Opens to one side and only has one metal hinge. Commonly used as an alternative to a buckle clasp.
- Security: Opens to one side and has an additional flap to keep the watch secure. Fastened to the watch with a spring bar.
- Buckle: A standard on watch straps that are made of leather and textiles. Similar to a belt, they open and close by adjusting the buckle pin, and can be plated in different colors.

Watch clasps keep your watch securely
fastened to your wrist. Here, we’ve rounded up
different types you may encounter while watch
shopping.
- Butterfly: Similar to a butterfly spreading its
wings, the butterfly clasp opens to both the
right and left. Found on most bracelet watches. - Flip: Opens to one side and only has one
metal hinge. Commonly used as an alternative
to a buckle clasp. - Security: Opens to one side and has an
additional flap to keep the watch secure.
Fastened to the watch with a spring bar. - Buckle: A standard on watch straps that are
made of leather and textiles. Similar to a belt,
they open and close by adjusting the buckle
pin, and can be plated in different colors.









